

Due to the fundamentally different operation principles, theoretical methods for describing semiconductor physics are applicable only with considerable restrictions. Although there are important differences between the two types of devices, there are also many similarities that will be pointed out in the sections to follow. ylengthalongthechannelfrom thesourcecontact zwidthofthechannel x(y)channeldepth(varies c alongthelengthofthechannel). Short-channel effects comparable to those known from semiconductors were observed for devices with gate lengths smaller than 1 µm. The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Basics (Understandingwith Reading: Pierret 17.1-17.2 and Jaeger Notes ath) 4.1-4.10 and OSTransistor CoordinateDefinitionsforour xdepthintothesemiconductor fromtheoxideinterface. Using a highest-standard epitaxial deposition system and state-of-the-art electron beam lithography, we succeeded in fabricating FETs with gate lengths as small as 60 nm. In this topic we describe an amplifier based on an n-channel JFET. For this we studied devices with various gate lengths fabricated from LaAlO 3-SrTiO 3 heterostructures. Like MOSFETs, JFETS are unipolar transistors, made in n-channel and p-channel versions.

We have fabricated and analyzed very small field effect transistors (FETs) built from complex oxides and explored the possible existence of short-channel effects. VGSth ) is kept constant and VDS is increased from 0 to a more positive voltage Enhancement-Type MOSFET Transfer Curve To determine ID given VGS: Where: VT = threshold voltage or voltage at which the MOSFET turns on k = constant found in the specification sheet 2 TGSD )VV(kI p-Channel Enhancement-Type MOSFETs The p-channel enhancement-type MOSFET is similar to the n-channel, except that the voltage polarities and current directions are reversed.Due to their wide spectrum of functionalities, complex oxides are highly interesting for use in electronic devices. Output characteristic curve for n-channel JFET \ MOSFET: +VGS turns the transistor OFF, while -VGS turns the transistor ON. Water analogy for the JFET control mechanism 6.2 JFET Construction Transfer characteristic curve of n- channel JFET: pinch off voltage: Vp Water analogy for the JFET control mechanism loss 8 Its operation is based on a controlled input voltage. Introduction of bipolar junction transistor, terminal characteristics, forward active bias, current gain. The MOSFET functionality was explained in the lecture Electronic. FET 6.2 JFET Construction VGS -Control the flow of water (charge) to the drain VDS -the applied voltage from drain to source like the source of water pressure. A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a three-terminal semiconductor device. The first FET transistors used metal gate electrode.
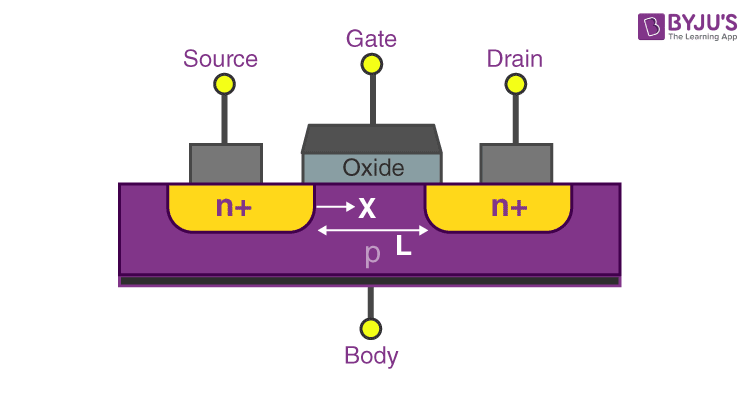
We will derive some current-voltage equations for the transistor. The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. FETs are less sensitive to temperature variations and because of their construction they are more easily integrated on ICs. We begin with the physical structure and a qualitative understanding of how.FETs also have a higher input impedance.

FETs are voltage controlled devices whereas BJTs are current controlled devices.
#FET TRANSISTOR LECTURE PDF#
Download ch6 Field-Effect Transistors.ppt and more Engineering Lecture notes in PDF only on Docsity!Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors FETs (Field-Effect Transistors) are much like BJTs (Bipolar Junction Transistors).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
